

“Wi-Fi booster” is often used by manufacturers as a marketing term that covers any device that amplifies or extends a Wi-Fi signal. The Key Differences Between Wi-Fi Boosters and Wi-Fi Extendersĭefining the differences between Wi-Fi boosters and extenders is a difficult task for a simple reason: Wi-Fi extenders are often classified as Wi-Fi boosters. Electrical devices, walls, and floors will have no impact on the strength of the signal transmitted to a Wi-Fi extender.

This means they’re not subject to the same types of interference as boosting devices that connect to your route wirelessly. Wi-Fi extenders connect directly to your router using an ethernet or coaxial cable. The extender then creates a new Wi-Fi channel for you to connect to, which should come close to matching the speeds achieved when you connect a device directly to the router. For example, you may place an extender in a bedroom that achieves patchy reception from your router. They achieve this by creating a new wireless channel for you to connect your devices. But instead of amplifying the signal, an extender rebroadcasts it, so it covers a larger portion of your property. Similar to Wi-Fi boosters, they connect to your router to pick up its wireless signal.
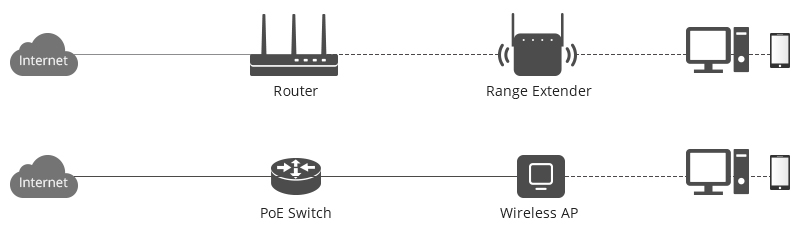
#Wifi repeater vs extender install#
Wi-Fi extenders install between your router and any area of your home where you want improved Wi-Fi coverage. However, they also usually require long wires, which can be unwieldy. This eliminates the possibility of interference from electrical devices, ensuring you always have a strong connection speed. Wired boosters connect directly to your router’s coaxial cable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
